Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate
Explore CS and DS Chains
Chondroitin Sulfate (CS) and Dermatan Sulfate (DS) are linear anionic polysaccharides that are widely found on the cell surface and in the cell matrix and connective tissue. CS and DS chains are usually attached to core proteins, forming proteoglycans (PGs). CS and DS exhibit different sulfation patterns and variable sequence arrangements, and their molecular weights also vary within a large range, increasing the structural complexity and diversity of CS/DS. The structure and function of CS/DS PGs involves them in a variety of physiological and pathological processes.
For more on Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate, see our pages on Purified Glycosaminoglycans, Chondroitin Sulfate Antibodies and Chondroitinase Enzymes. See also our Glycobiology home page.
Chondroitin Sulfate & Dermatan Sulfate Structural Variation
- The only structural difference between Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate is related to the presence of IdoA in the latter.
- Both types of GAG chains are extensively sulfated by 4-O and 6-O sulfation on GalNAc and 2-O sulfation on GlcA and IdoA.
- The pattern of sulfation can be determined after digestion with bacterial chondroitinases.
- These enzymes release the disaccharide GlcA/IdoA(b1-3) GalNAc with different sulfation patterns.
- The major types of sulfated polysaccharides are defined by the letters A to E.
- These variations in sulfation patterns confer different roles to CSs by promoting selective interactions with different molecules.
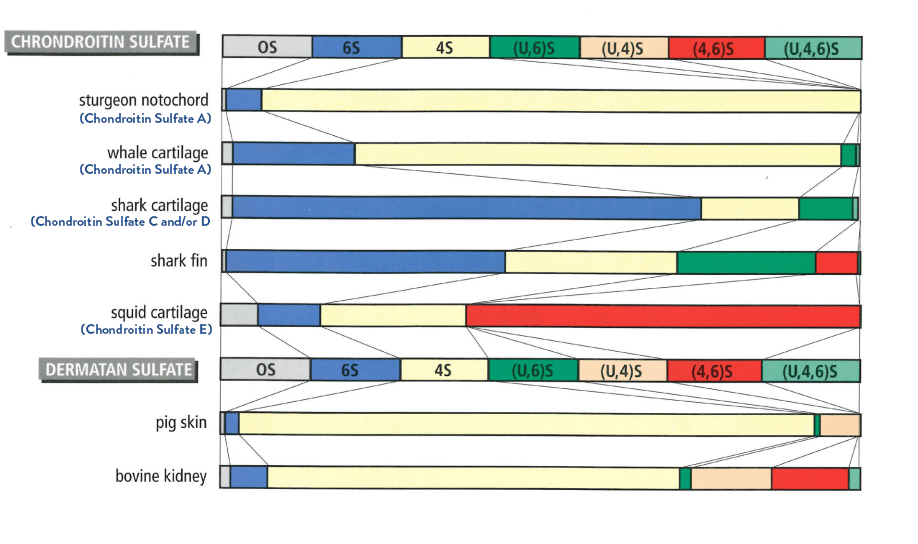
Structural Variability of Chondroitin Sulfate & Dermatan Sulfate
AMSBIO is proud to support the glycobiology / Proteoglycan research community with a suite of products for the different sulfation patterns of Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate.
| Letter identification | Dermatan Sulfate (formerly Chondroitin Sulfate B) | Chondroitin Sulfate A | Chondroitin Sulfate C | Chondroitin Sulfate D | Chondroitin Sulfate E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site of sulfation | Various | Carbon 4 of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) sugar | Carbon 6 of the GalNAc sugar | Carbon 2 of glucuronic acid and 6 of GalNAc sugar | Carbons 4 and 6 of GalNAc sugar |
| Systematic name | DS | C-4-S | C-6-S | C-2,6-S | C-4,6-S |
| AMSBIO Antibody Offering | |||||
| Monoclonal antibodies recognising undigested GAG: | 2H6, LY111, CS-56 | 2H6, LY111, CS-56 | MO-225 | ||
| CS Stub Antibodies recognizing 0S,4S,6S | 2B6 (after digestion with Chondroitinase B) | 2B6 | 3B3 | ||
| Enzyme Activity against different classes / sulfation patterns. | Chondroitinase B | Chondroitinase AC Enzymes (Flavo, Arthro) | |||
| Chondroitinase ABC catalyses the removal of CS and DS side chains of CSPGs with some activity against HA. | |||||
| AMSBIO Carbohydrate Offering | |||||
| Disaccharides | Yes | ||||
| Oligosaccharides | Yes | Yes (CS-AC oligos) | Yes | Not Yet | |
| Polysaccharides | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Can't find what you need?
Please contact us with any inquiries regarding our carbohydrate-related products
- Caterson, B. (2012). Fell‐Muir Lecture: chondroitin sulphate glycosaminoglycans: fun for some and confusion for others. International journal of experimental pathology, 93(1), 1-10.
- Djerbal, L., Lortat-Jacob, H., & Kwok, J. C. F. (2017). Chondroitin sulfates and their binding molecules in the central nervous system. Glycoconjugate journal, 34(3), 363-376.
- Mishra, S., & Ganguli, M. (2021). Functions of, and replenishment strategies for, chondroitin sulfate in the human body. Drug Discovery Today, 26(5), 1185-1199.