Heparanase and Hyaluronidase Activity Kits
Effectively measure enzyme activity
AMSBIO supplies Razie assay kits (Heparanase and Hyaluronidase Activity Assay Kits) to measure enzyme activity of heparanase and hyaluronidase, respectively, in cell culture supernatants, human plasma, biological fluids and tissue samples. Our kits have been used for research into anti-inflammatory responses, kidney disease and cancer research. Heparanase and hyaluranidase enzymes both play an important role in the extracellular matrix (ECM). Our kits provide a solution to the performance and standardization problems found with traditional measurement techniques used for these types of enzymes.
Each assay is available in two formats:
- with enzyme as positive control to demonstrate digestion/activity.
- without positive control, for end-users who have their own enzyme for use as positive control.
These enzyme activity assays are complementary to our ELISA kits. ELISA kits measure the quantity of a particular antigen as detected by specific antibodies (and will give you an answer that includes inactive forms of the enzyme in question) – while these activity assays measure the activity of relevant enzymes in the system as assessed by substrate degradation.
See papers by Martin et al ( 2015, 2017) below where they used our heparanase activity assay alongside one of our heparanase ELISAs to measure both quantity and activity of heparanase enzymes in their system.
Features
- Suitable for inhibitor screening
- Non-radioactive
- Fast and easy to use
- Sensitive and specific
- Use universal 96-well plate format ideal for inhibitor studies
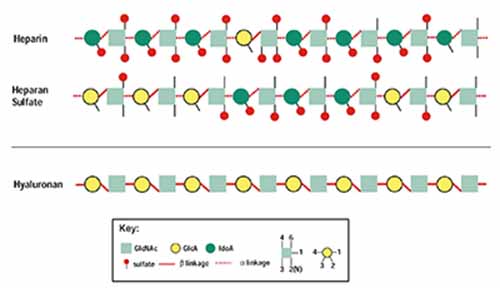
Glycosaminoglycan Substrates
Heparanase Assay Kit
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) are known to play important structural and functional roles in linking the component proteins of the basement membrane, controlling membrane permeability properties and signal transduction. This latter function is achieved by controlling the bioavailability of cytokines and growth factors to their cellular receptors. HSPG on the cell surface participates in signal transduction by facilitating the interaction between growth factors and their receptors. Heparanase is an endoglycosidase that specifically cleaves heparan sulfate (HS) side chains of HSPG.
Due to the wide distribution and functions of HSPG, heparanase activity affects various cellular functions under normal and pathological conditions.
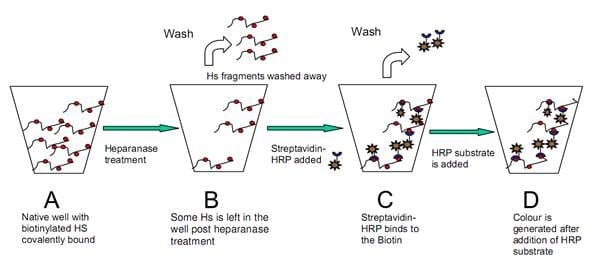
Research into the development of inhibitors or enhancers of this enzyme had been previously obstructed by the lack of sensitive and specific tests for human heparanase activity. Furthermore the unavailability of a purified enzyme or instability of the cloned enzyme limits assay design. To date the available tests have the above shortcomings and are time consuming, not applicable for inhibitor screening or lack an appropriate positive control. The heparanase assay kits below have been specifically developed to overcome these problems.
Heparanase assay workflow
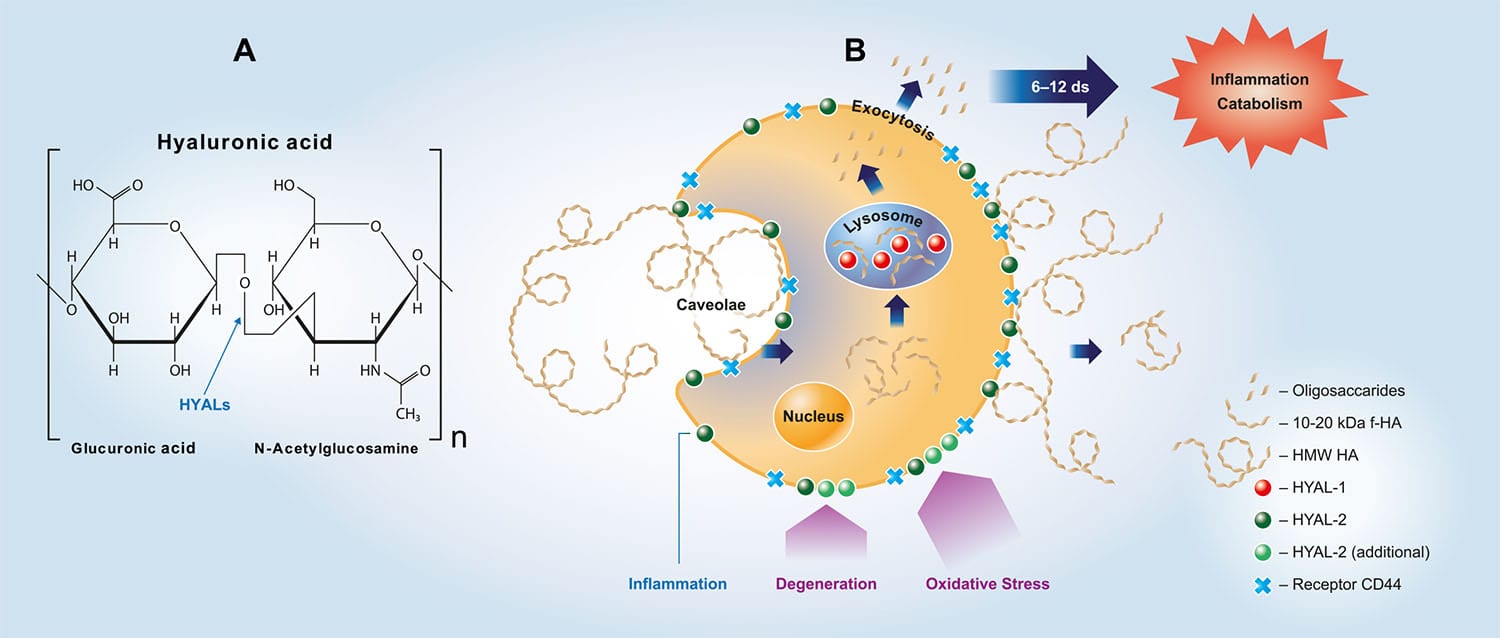
Hyaluronidase Assay Kit
Hyaluronic Acid is an important structural macromolecule in the ECM, and involved in the interaction of matrix components. Mammalian hyaluronidases (HYAL1 to HYAL4) are ECM enzymes that degrades hyaluronic acid via hydrolysis of the 1-4 bond between N-acetyl glucosamine and D-glucuronic. Mammalian hyaluronidases can also cleave similar glycosaminoglycans.
Our Razie mammalian hyaluronidase assay kits can be used for screening hyaluronidase inhibitors and for quantification of hyaluronidase activity. The principles of the kit are very similar to the heparanase assay kit. Adaptations are available to measure the activity of bacterial hyaluronidase enzymes.
The HYAL activity kit (Ra003-01-HAK) from AMSBIO helped us to move from purely analyzing HYAL (gene/protein) expression to actually measuring HYAL activity. When investigating enzymes, such a functional read-out is crucial. While well-established methods and kits exist for other enzymes such as MMPs, determining HYAL activity is more complicated. Although our treatments did not result in a significant increase in HYAL activity, we found the assay to be reliable and very easy to use.
Citations
Expression and activity of hyaluronidases HYAL-1, HYAL-2 and HYAL-3 in the human intervertebral disc.
Krupkova, O.,Greutert, H., Boos, N et al (2019) European Spine Journal, 1-11
(Note that our Chondroitinase ABC has also been to model intervertebral disc degeneration).
The Effects of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles on an Enzymatic Reaction Between Horseradish Peroxidase and 3, 3', 5, 5'-Tetramethylbenzidine.
Morris, B., & Behzad, F. (2014) Biochemistry & Pharmacology: Open Access, 2014.
The Effects of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles on an Enzymatic Reaction
Between Horseradish Peroxidase and 3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine
Morris, B & Behzad, F., (2014) Biochemistry & Pharmacology: Open access, 3(6):
The β-D-endoglucuronidase heparanase is a danger molecule that drives systemic inflammation and correlates with clinical course after open and endovascular thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair: Lessons learnt from mice and men.
Martin, L., Gombert, A., Chen, J., Liebens, J., Kalder, J., Marx, G., ... & Schuerholz, T. (2017). Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 681.
This paper cites Ra001-BE-K (Heparanase Activity Assay Kit with Positive Control Enzyme), alongside AMS.E03H0100 (ELISA to measure quantity of Mouse Heparanase) and AMS.E0623Ge (General ELISA Kit for Heparan sulfate)
The Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptide 19-2.5 Interacts with Heparanase and Heparan Sulfate in Murine and Human Sepsis
Martin, L., et al (2015) PloS one 10(11): e0143583.
Heparanase Is Essential for the Development of Acute Experimental Glomerulonephritis.
Garsen, M., et al (2016) The American Journal of Pathology 186(4): 805-815.
Endothelin-1 induces proteinuria by heparanase-mediated disruption of the glomerular glycocalyx.
Garsen, M., et al (2016). Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 27(12), 3545-3551.
Vitamin D attenuates proteinuria by inhibition of heparanase expression in the podocyte
Garsen, M., et al (2015) The Journal of Pathology 237(4): 472-481.
Heparanase activity in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: implications for tumor invasion
Masola, V., et al (2009) BMC Cancer 9(1), 1
Heparanase and syndecan-1 interplay orchestrates FGF-2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells
Masola, V., et al (2011) Journal of Biological Chemistry, jbc-M111
Regulation of heparanase by albumin and advanced glycation end products in proximal tubular cells
Masola, V., et al (2011) Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 1813(8): 1475-1482