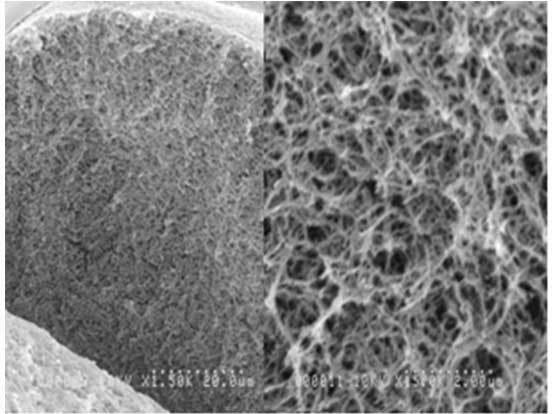
Features
Cellufine™ MAX IEX media are offered in six products (S-r, S-h, Q-r, Q-h, CM, & DEAE), including both anion and cation chemistries. Each offers excellent flow properties, mechanical stability and chemical resistance. These ion exchangers are ideally suited for both laboratory and process scale chromatography of proteins, peptides and other biomolecules. Applications include the purification of antibodies, growth factors, albumin, enzymes, and nucleic acids.
- Largest pore size of all Cellufine™ chromatography media- provides superior strength and excellent mass transfer
- Based on 90µm (average) highly cross-linked cellulose beads, surface-modified with dextran
- All operable at practical flow velocities (500cm/h) and pressures
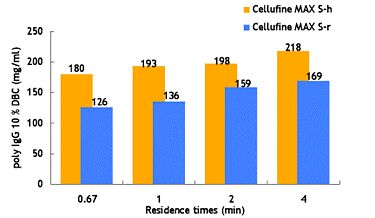
- Stable over a range of residence times
- Stable to chemicals, caustic and acidic solutions
Our Products
Properties of Cellufine™ MAX IEX Media
| MAX-CM | MAX S-r | MAX S-h | MAX DEAE | MAX Q-r | MAX Q-h | ||
| Matrix | Cross-linked cellulose with dextran scaffold | ||||||
| Particle Size (µm) | 40-130 | ||||||
| Ligand | CM | S | S | DEAE | Q | Q | |
| Ion Exchange Capacity (mEq/ml) | 0.09-0.22 | 0.12-0.24 | 0.13-0.25 | 0.14-0.25 | 0.13-0.20 | 0.17-0.24 | |
| 10%DBC (mg/ml) | Lysozyme | 220 | 144 | 191 | - | - | - |
| BSA | - | - | - | 197 | 141 | 225 | |
| Human-γ-globulin | 104 | 131 | 216 | 108 | 74 | 135 | |
| pH Stability | 2-13 | 2-13 | 3-14 | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-12 | |
| Storage | 20% Ethanol | ||||||
Cellufine resin was developed by JNC and is available from AMSBIO in EU and the US.
Structure
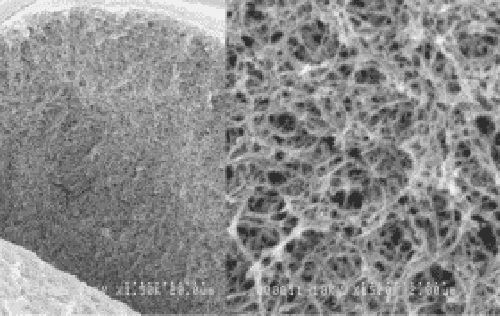
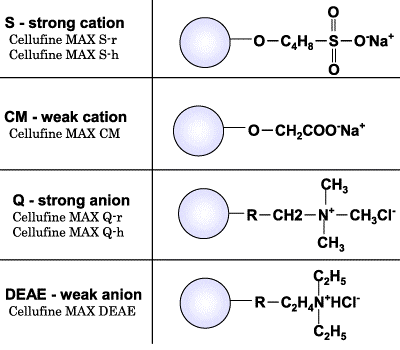
Subtypes of MAX S and Q
Two subtypes, h and r, are available for Cellufine™ MAX S and Q. The differences between the subtypes is due to the design of the media, with subtype h designed for higher binding capacity than subtype r, by optimizing the ligand content and dextran scaffold.
Subtype h: highest absorption capacity
Subtype r: high recovery, high resolution and robustness
Pressure-flow Properties
Cellufine™ MAX IEX media enable high-flow operation, which is essential for the efficient purification of biopharmaceuticals. The figures below show pressure-flow velocity curves of Cellufine™ MAX IEX media in a 30 cm column with a 20 cm bed height.
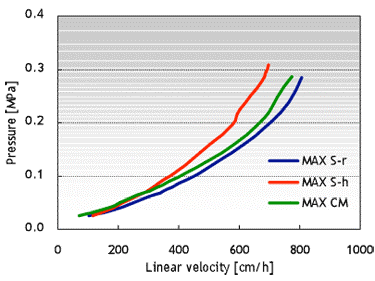
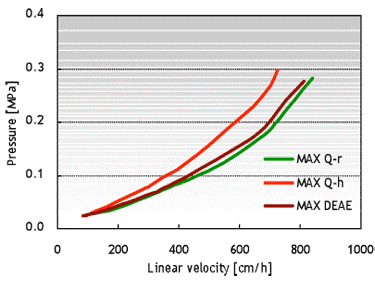
Fig. 3 Pressure-flow velocity curves for Cellufine™ MAX IEX media. Column: 30 cm I.D. x 20 cm L. Mobile phase: Pure Water at 24°C
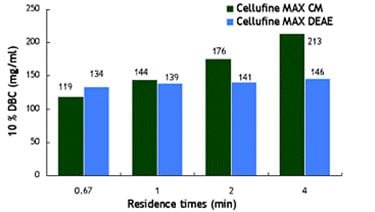
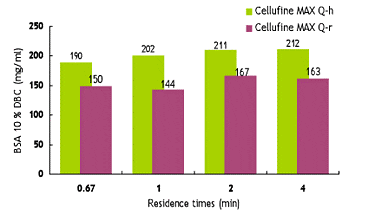
Dynamic Binding Capacities
Efficient mass-transfer characteristics of Cellufine™ MAX IEX media translate to superior dynamic binding capacities (DBC). Figures 4-6 show DBC of model proteins at different residence times for Cellufine™ MAX IEX media. All Cellufine™ MAX IEX media are stable over a range of residence times.
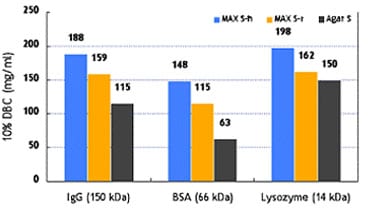
Fig. 7 shows that Cellufine™ MAX S exhibits superior dynamic binding performance across a range of protein characteristics compared to competitive media.
These unique characteristics of Cellufine™ MAX IEX media make it suitable for use in upstream as well as downstream steps in biopharmaceuticals purification.
Cellufine™ MAX Weak Ion Exchange Media
Cellufine™ MAX Anion Exchange Media
Cellufine™ MAX Cation Exchange Media
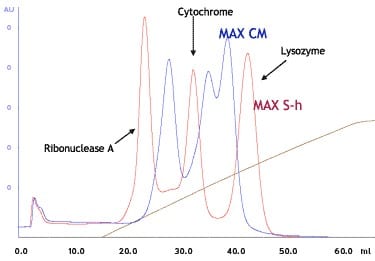
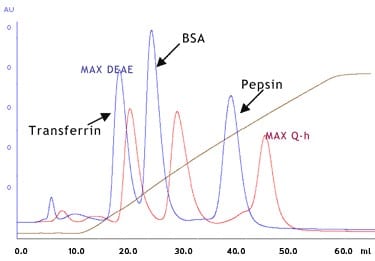
Model Protein Separation
Cellufine™ MAX IEX media are optimized for high adsorption and high resolution. Model protein separation with MAX S-h and MAX CM (strong cation vs. weak cation) and MAX Q-h and MAX DEAE (strong anion vs. weak anion) are shown below.
Cellufine™ is the trademark of JNC Corporation, Tokyo, Japan