HVEM-LIGHT-BTLA Pathway
Important cosignaling pathways in immune regulation
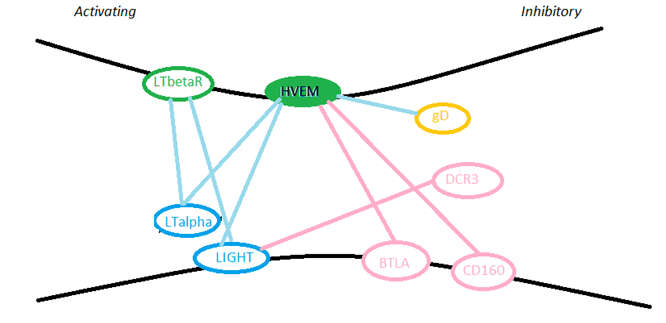
The checkpoint receptors HVEM, LIGHT, and BTLA are part of a complex network of overlapping receptor interactions that function in both immune stimulation and suppression.
AMSBIO supplies a wide range of HVEM products for use in immuno-oncology research including recombinant HVEM, LIGHT, and BTLA proteins, BTLA:HVEM and LIGHT:HVEM Inhibitor Screening Assay Kits, and HVEM and LIGHT-expressing cell lines.
What is HVEM?
Herpes Virus Entry Mediator (HVEM), also known as CD270 or TNFSFR14 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily Member 14), is a cell surface receptor expressed on many immune cells, including T cells.
HVEM plays a role in herpes simplex virus infection—the interaction between HVEM and the viral protein Glycoprotein D (gD) is one of the first steps of herpes simplex virus (HSV) entry into the cell.
HVEM in Cancer
HVEM has also become an important immuno-oncology target after researchers discovered that HVEM is involved in the induction of apoptosis of tumor cells.
When HVEM interacts with a protein known as LIGHT (TNFSF14, CD258), it creates a co-stimulatory signal that activates lymphoid cells and amplifies the immune response. This means HVEM/LIGHT binding combines immune system amplification with a pro-apoptotic effect, providing a two-pronged attack against cancer, and therefore making it a particularly promising target for cancer drug discovery.
HVEM also can bind to a protein called BTLA (CD272, IgSF), which negatively regulates T-cell immune responses. Thus, HVEM acts as a molecular switch, either activating or inhibiting the immune response, depending on which ligand it binds.