Prostate cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer in males and is responsible for claiming the lives of more than 350,000 men globally each year. The first line of treatment for advanced prostate cancer is Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). However, despite the effectiveness of ADT, most tumours eventually progress into an aggressive stage known as castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), at which point ADT is ineffective.
miRNA: Alleviating Anxiety in the Amygdala
June 6, 2023
Sustainability Month: Some Options for a Greener Lab
April 11, 2023Unfortunately, nearly all men affected by CRPC also experience resistance to second-generation agents targeting the androgen signalling axis, creating an urgent need for new and innovative treatments for advanced prostate cancer.
Almost every type of cancer has cancer-associated glycans, which are a defining characteristic of cancer cells. These glycans have enormous promise for the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic targets in the fight against cancer. Dr. Jennifer Munkley and her colleagues at the Newcastle Centre for Cancer have identified a specific enzyme, called GALNT7, which is upregulated in prostate cancer and drives tumour growth. Using the Oris Pro 96-well Invasion Assay from AMSBIO, Dr Munkley and her fellow researchers discovered that GALNT7 increases prostate cancer cell migration and invasion.

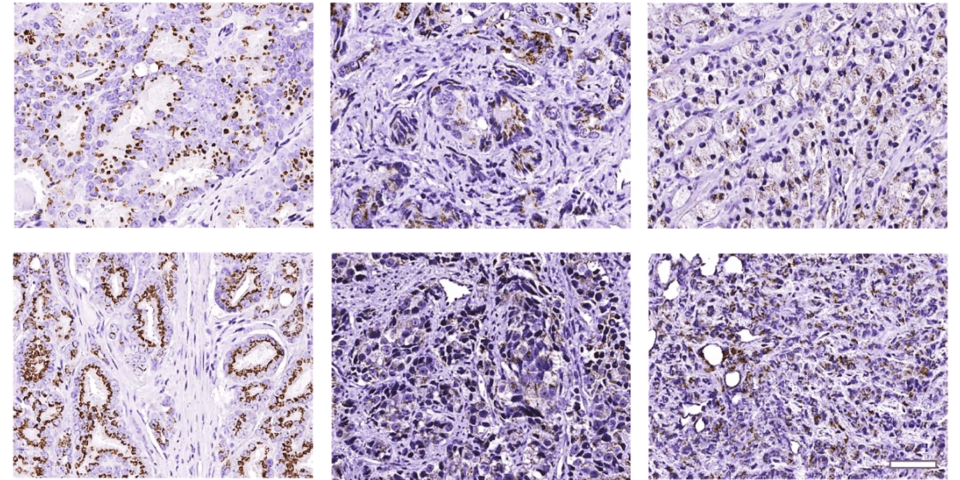
Fig 1. Immunohistochemical analysis of GALNT7 protein in a tissue microarray containing matched tumour and normal tissue from the same patient, demonstrating increased GALNT7 protein in the tumour tissue relative to the normal tissue. Figure adapted from Scott, E., Hodgson, K., Calle, B. et al. Upregulation of GALNT7 in prostate cancer modifies O-glycosylation and promotes tumour growth. Oncogene 42, 926–937 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-023-02604-x. (Previously published by Vidal, I. et al. (2021). GSTP1 positive prostatic adenocarcinomas are more common in Black than White men in the United States. PLOS ONE, 16(6), e0241934. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241934)
Key Findings of GALNT7 in prostate cancer:
- Upregulation in prostate cancer – Dr Munkley and colleagues’ analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas Adenocarcinoma cohort and two primary patient cohorts identified upregulation of the GALNT7 gene in prostate cancer tissue. Additionally, tissue analysis revealed that GALNT7 protein expression was significantly elevated in prostate cancer tissue compared to normal prostate tissue.
- Upregulation in urine and blood samples from men with prostate cancer – The study found that men with prostate cancer had significantly higher levels of GALNT7 in their urine and plasma samples compared to men without the disease. Interestingly, urine samples containing GALNT7 were slightly more effective than the traditional prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test in diagnosing prostate cancer. Combining both PSA and GALNT7 increased the diagnostic accuracy even further. These findings suggest that GALNT7 could be a useful biomarker for prostate cancer diagnosis, potentially improving the accuracy of current screening methods.
- Elevated GALNT7 expression in CRPC patients which declines with ADT- In patients with advanced prostate cancer, the levels of GALNT7 are higher, but they decrease when they undergo a particular type of therapy called androgen deprivation therapy. This suggests that measuring GALNT7 levels could help identify patients who may relapse with a more aggressive form of the disease. This could be helpful in predicting and monitoring the progression of prostate cancer.
- Modification of O-glycosylation – GALNT enzymes play a role in a process called O-glycosylation, which involves adding sugar molecules to proteins. This creates the Tn antigen linked to tumour growth and poor prognosis for cancer patients. GALNT7 alters O-glycosylation in prostate cancer cells, causing overexpression of Tn antigen, which may contribute to the development and spread of prostate cancer.
- Promotion of prostate tumour growth – Upregulation of GALNT7 promoted prostate cancer cell proliferation in vivo, while knockdown resulted in the opposite effect. GALNT7 also enhances prostate cancer cell invasion and migration in vitro, which was investigated using the Oris 96-well Invasion Assay from AMSBIO.
- Correlation of GALNT7 expression with cell cycle and immune signalling pathways – FOXO1 is a protein involved in cell cycle regulation, but it is often lost in prostate cancer. Dr. Munkley and her colleagues discovered that higher levels of GALNT7 in prostate cancer cells led to a decrease in FOXO1 protein levels. Additionally, the researchers analyzed a cohort of patients with metastatic CRPC and found that higher levels of GALNT7 were associated with decreased activity in seven different pathways involved in the immune system.
Dr Munkley and her fellow researchers have revealed that GALNT7 could serve as a biomarker for prostate cancer. They have also shown that GALNT7 has great potential to improve the accuracy of diagnostics for this disease. Additionally, its involvement in the development and spread of prostate cancer indicates that GALNT7 could be a target for innovative therapies for advanced prostate cancer. AMSBIO supply an extensive range of cancer research tools, including the Oris 96-well Invasion Assay, primary cell lines and tissues. To find out more about how we can aid in the advancement of your research, visit our page on Cancer Research page here.
Further reading
Upregulation of GALNT7 in prostate cancer modifies O-glycosylation and promotes tumour growth.
Scott, E., Hodgson, K., Calle, B. et al. Oncogene 42, 926–937 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-023-02604-x