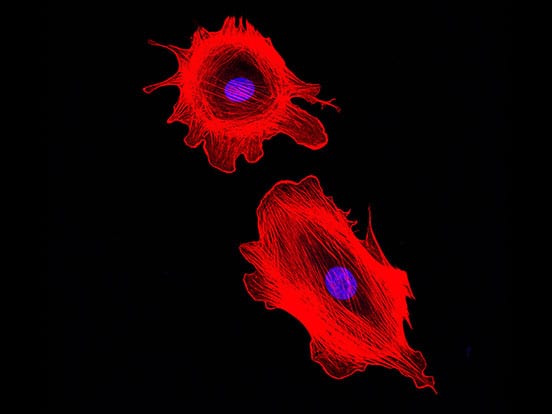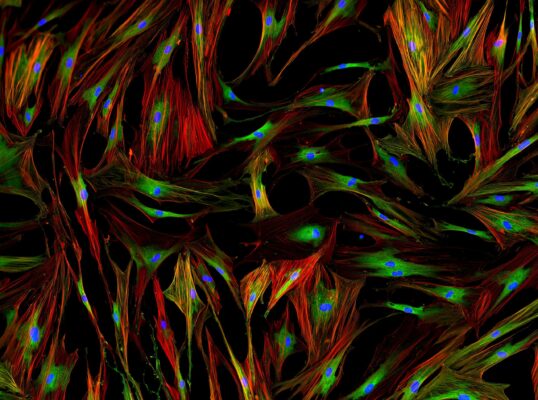
Human Normal Primary Cells
Physiologically relevant tools for cell culture
Cultured directly from living tissue or blood cells, primary cells offer a physiologically relevant tool for a multitude of applications in life sciences research. Isolation of primary cells is a notoriously time-consuming and resource-intensive process so let us do this bit for you.
AMSBIO supplies a unique range of human primary cells from multiple organs including the lung, liver, intestine, and kidney. Search our available specified cell types to find primary cell solutions for your research.
Benefits
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for long-term testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh primary cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Characterization: cells have been extensively characterized by morphology, and surface/ internal marker expression
- More comprehensive donor information
Applications
Intestinal Primary Cells:
- Toxicology pertaining to oral medication • Toxicity • Drug screening •Absorption studies • Gene expression.
Kidney Primary Cells:
- Function and pathophysiology of the kidney • Toxicity • Drug transporter research • Tissue engineering • Single-cell analysis of individual donors • Kidney disease progression • Urine regulation
Liver Primary Cells:
- Induction • Toxicity • Drug metabolism • Drug screening • Drug transporter activity • Drug-drug interaction • Bile production and absorption • Chronic liver injury
Lung Primary Cells:
- Single-cell analysis from individual donors • Investigating the function and pathology of the respiratory system • Drug discovery cell screening for in vitro assay of compounds • 3D tissue model
What are Primary Cells?
Primary cells are cells isolated directly from living tissue (e.g. biopsy material) using enzymatic or mechanical methods and established for growth in vitro.
These cells have undergone very few population doublings and are therefore more representative of the main functional component of the tissue from which they are derived in comparison to continuous (tumor or artificially immortalized) cell lines.
With comprehensive donor information made available with primary cells, researchers acquire the ability to study donor variability and not just the cells. The tissue complexity and donor variability, which is difficult to replicate in cell lines since they are very uniform in nature, is a great advantage of using primary cells for research particularly in the field of personalised medicine.
Intestinal Primary Cells
Primary Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells are isolated from the ascending colon, descending colon, transverse colon, Jejunum and duodenum.
The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of epithelial cells and are characterized by viability, morphology, plating efficiency along with cell characterization by staining for CK8 and CK18.
In addition, each lot will be tested for its ability to maintain function for a minimum period of 5-7 days and will be reported on the quality control report delivered with each vial.
Applications
- Toxicology pertaining to oral medication • Toxicity, drug screening, absorption studies, and gene expression. • Laboratory research use only.
Advantages
- Investigation of several GI diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), colon and gastric cancer.
- Our intestinal epithelial cells can be used to study disease mechanism, drug compounds, and modulators from various regions of the intestine.
- Using AMSBIO’s Intestinal Epithelial cell media, the epithelial cells can be maintained for as long as 5-7 to use to study gene expression, metabolism, and drug absorption.
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Ascending Colon | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Descending Colon | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Duodenem | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Ilium | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Jejunum | Minimum of 500k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Transverse Colon | 800k | View |
Primary Human Intestinal Myofibroblast cells are isolated from whole adult human intestines that are suitable for transplantation. The myofibroblasts are isolated from the descending colon, ascending colon, duodenum, jejunum, ileum and transverse colon.
The cell composition consists of a heterogenous population of myofibroblasts distinctly from the above region and the cells are tested for viability, morphology, and attachment efficiency (by Crystal Violet).
Myofibroblasts are characterized by immunofluorescent staining positive for alpha smooth muscle actin and negative for desmin.
Applications
- Toxicology pertaining to oral medication • Toxicity, drug screening, absorption studies, and gene expression. • Laboratory research use only.
Advantages
- Investigation of several GI diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), colon and gastric cancer.
- Using AMSBIO's Intestinal Myofibroblast cell media, the myofibroblast cells can be maintained for as long as 5-7 to use to study gene expression, metabolism, and drug absorption.
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Intestinal Myofibroblast Ascending Colon | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Myofibroblast Descending Colon | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Myofibroblast Duodenem | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Myofibroblast Ileum | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Myofibroblast Jejunum | 800k | View |
| Normal Human Intestinal Myofibroblast Tranverse Colon | 800k | View |
Kidney Primary Cells
Normal Human Glomerular Endothelial Cells (NhGEC) are specialized microvascular cells that make up the innermost layer of the glomerular filtration barrier. They are separated from podocytes by a thin layer of glomerular basement membrane. These cells exhibit cobblestone morphology at confluence and present fenestrations specific of this cell type.
The NhGEC will be evaluated for the expression of endothelial specific markers (e.g. CD31, vWF and Ve-Cadherin) by immunofluorescence.
NhGEC can be expanded between 5 to 8 passages, while maintaining their particular characteristics.
NhGEC are terminally differentiated cells and present no significant differentiation capacity.
Applications
- Ideal in studies of: function and pathophysiology of the kidney • toxicity • drug transporter research • tissue engineering • single-cell analysis of individual donors • kidney disease progression
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for long-term testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh glomerular endothelial cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Characterization: cells have been extensively characterized by morphology, and surface/ internal marker expression
- More comprehensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Glomerular Endothelial Cells | 500k | View |
Cryopreserved Human Kidney Cortical Cell Mix is a heterogeneous cell mixture isolated from the cortex of human kidneys after removal of the kidney capsule and medulla.
Mixes can be utilized to study heterogeneous kidney populations, or be further processed into homogenous cell populations.
Major cell types include but are not limited to: • Proximal tubules • Distal tubules • Endothelial cells (including glomerular endothelial cells) • Mesangial cells • Podocytes • Interstitial fibroblasts • Epithelial Bowman’s Capsule Cells • Residing renal adult progenitor cells • Juxtaglomerular cells
Applications
- Human Kidney Cortical Cell Mixes are ideal in studies of: function and pathophysiology of the kidney • toxicity • drug transporter research • tissue engineering • cell population analysis from individual donors • homogenous cell population isolation by FACS or magnetic sorting • urine regulation
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh cortical cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- Versatility: various cell types can be studied or selected/ expanded from cortical cell mixes
- Characterization: cells have been extensively characterized by attachment, viability, and surface/ internal marker expression
- More comprehensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Kidney Cortical cells UMIX population | 500k | View |
Cryopreserved Human Kidney Mesangial Cells are isolated from the cortex of human kidneys that are deemed not suitable for transplantation.
After digestion of the cortex, a pure population of mesangial cells is isolated by magnetic positive selection for PDGFRβ. These cells “fill the gap” between adjacent capillary loops surrounded by the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and the podocytes.
Mesangial cells remove trapped residues and aggregated protein from the basement membrane. In addition, they aid filtration by constituting part of the glomerular capillary tuft structure that filters fluids to produce urine.
Homogeneous cultures of Mesangial cells resemble smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts. On average, 15–20 passages in culture can been obtained from NhKM cells.
Applications
AMSBIO's Mesangial cells are ideal in studies of: function and pathophysiology of the kidney • toxicity • drug transporter research • tissue engineering • single-cell analysis of individual donors • capillary flow in the renal system • urine regulation
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for long-term testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh cortical cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Characterization: cells have been extensively characterized by morphology, functionality, and surface/ internal marker expression
- More comprehensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Kidney Mesangial Cells | 500k | View |
Cryopreserved Primary Human Kidney Podocytes are isolated from the cortex of human kidneys.
Podocytes are obtained after singular glomerular isolation and digestion. A pure population of podocytes is isolated by magnetic positive selection.
Podocytes are terminally differentiated cells found lining the outer surface of the glomerular capillaries. They have foot projections that form the slit diaphragm to allow ultrafiltration of the blood based on size and charge, and allows the filtration of cationic molecules, electrolytes, and small and midsized solutes while restricting the passage of anionic molecules and macromolecules.
Podocytes cannot be cultured for more than 1 or 2 passage without loss of their particular traits (like foot processes and expression of slit diaphragm proteins).
Applications
AMSBIO's Podocytes are ideal in studies of: function and pathophysiology of the kidney • toxicity • drug transporter research • tissue engineering • single-cell analysis of individual donors • kidney disease progression
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh cortical cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Characterization: cells have been extensively characterized by morphology, functionality, and surface/ internal marker expression
- More comprehensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Kidney Podocytes (3 additional vials/ampules will be shipped per cell vial: Cholecalciferol-100 nM , ATRA-1?M, and dexamethasone-100nM) | 100k-200k | View |
| Normal Human Kidney Podocytes (3 additional vials/ampules will be shipped per cell vial: Cholecalciferol-100 nM , ATRA-1?M, and dexamethasone-100nM) | 250k-400k | View |
| Normal Human Kidney Podocytes (3 additional vials/ampules will be shipped per cell vial: Cholecalciferol-100 nM , ATRA-1?M, and dexamethasone-100nM) | 50k-99k | View |
Cryopreserved Human Kidney Proximal Tubules Cells are isolated from the cortex of human kidneys after removal of the kidney capsule and medulla.
After digestion of the cortex, proximal tubules are isolated by magnetic positive selection as a pure population.
An integral part of the nephron, proximal tubule cells regulate the pH of the filtrate by exchanging hydrogen ions for bicarbonate ions in the filtrate; they are also responsible for secreting organic acids, such as creatinine and other bases, into the filtrate.
NhKPT cells are terminally differentiated and can be expanded for at least 15 population doublings.
Applications
AMSBIO's Kidney Proximal Tubule cells are ideal in studies of: function and pathophysiology of the kidney • toxicity • drug transporter research • tissue engineering • single-cell analysis of individual donors • ion channels • kidney disease progression
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh cortical cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Characterization: cells have been extensively characterized by morphology, functionality, and surface/ internal marker expression
- More comprehensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Kidney Proximal Tubule Cells | 500k | View |
Liver Primary Cells
Cryopreserved, Plateable Primary Human Hepatocytes are isolated from whole human livers that are not suitable for liver transplantation.
The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of hepatocytes which are characterized by viability, morphology, plating efficiency and various functional testing including multiple CYP450 basal and induction levels including CYP3A4, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP1A2, and CYP2B6.
In addition, AMSBIO's primary human hepatocytes will undergo an ECOD study for 7-HCG and 7-HCS formation, and finally each lot will be tested for its ability to maintain function for a minimum period of 5 days and will be reported on the quality control report delivered with each vial.
Applications
AMSBIO's Plateable Primary Human Hepatocytes can be used for • induction •toxicity • drug metabolism •drug screening • drug transporter activity • drug-drug interaction.
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for long-term testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh hepatocytes to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- Large lot sizes
- High post-thaw viability and yield
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
Characterized Cryopreserved Suspension Primary Human Hepatocytes are isolated from whole human livers that are not suitable for liver transplantation.
The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of hepatocytes which are characterized by viability, morphology, plating efficiency and the following enzyme panel: CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4 (midazolam), CYP3A4 (testosterone), GEN, SULT, UGT, and AO.
Applications
AMSBIO's primary human hepatocytes can be used for various short-term studies such as phase I and phase II metabolism, toxicity, drug-drug interaction, among other uses.
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh hepatocytes to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- Large lot sizes
- High post-thaw viability and yield
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
Cryopreserved Primary Human Cholangiocytes, also known as Intrahepatic Biliary Epithelial Cells, are isolated from whole human livers that are deemed not suitable for liver transplantation and have received consent to be donated for research.
Cholangiocytes are epithelial cells that line the bile ducts. They function primarily in the modification of bile. The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of cholangiocytes.
Applications
AMSBIO's human cholangiocytes are ideal in studies of: co-cultures and 3D cultures • toxicity • bile production and absorption • bile duct fibrosis • hormone signaling • cholangitis • cholangiocarcinoma • among many others
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh cholangiocytes to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Co-culturing
- Passaged: more hardy, greater number of cells than P0
- Ability to passage further
Cryopreserved Primary Human Hepatic Kupffer Cells are isolated from whole human livers that are deemed not suitable for liver transplantation.
Kupffer cells are the largest population of innate immune cells in the liver. They function in the removal of pathogens and the regulation of anti-viral immunity.
The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of Kupffer cells that are frozen down at passage 0 and are characterized by viability, morphology, plating efficiency, and FACS analysis.
Applications
AMSBIO's Kupffer cells are ideal in studies of: chronic liver injury • toxicity • inflammatory response activation • cell-cell signaling • NAFLD and NASH progression • co-culturing among many others.
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh Kupffer cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Co-culturing
- More extensive donor information
Cryopreserved Primary Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells are isolated from whole human livers.
Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells line the blood vessels of the liver. These cells play a role in thrombosis, the transportation of metabolites, inflammation, and angiogenesis.
Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells are also known to contribute to the initiation of chronic liver disease and to the activation of stellate cells. The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells.
Applications
AMSBIO's human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells are ideal in studies of: chronic liver injury • toxicity • immune response • portal vein fibrosis • angiogenesis • co-culturing • liver regeneration • stellate cell activation among many others.
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for long-term testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh sinusoidal endothelial cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High yield
- Co-culturing
- Passaged: more hardy, greater number of cells than P0
- More extensive donor information
Cryopreserved Human Hepatic Stellate Cells are isolated from whole human livers.
Stellate cells function in the storage of retinoid when in the quiescent state. Upon activation, stellate cells differentiate into fibroblast-like cells and are responsible for the production of collagen I and development of fibrosis.
The cell composition consists of a homogenous population of hepatic stellate cells and is characterized by viability, morphology, plating efficiency, and FACS analysis.
Applications
AMSBIO's stellate cells are ideal in studies of: chronic liver injury • toxicity • activation and differentiation • NAFLD and NASH initiation and progression • co-culturing • fibrosis among many others.
Advantages
- Reproducibility: same donor can be used for longterm testing
- Convenience: no waiting for fresh stellate cells to become available and the cryopreserved vials are not time-sensitive
- High post-thaw yield
- Co-culturing
- Passaged: more hardy, greater number of cells than P0
- More extensive donor information
Lung Primary Cells
Proliferating Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells- P0 (NhBE-P0) are isolated from the bronchus at the bifurcation point to the fourth generation of bronchi. The cell composition consists of undifferentiated ciliated, non-ciliated, goblet, and basal cells.
Proliferating NhBE-P0 cells have been characterized and Air/Liquid Interface culture (ALI) validated by immunofluorescence using protein markers for Cilia (acetylated tubulin), mucin (MUC5AC), tight junctions (Zonula Occludens-1), and basal cells (cytokeratin-5).
The NhBE-P0 cells are guaranteed to have minimum population doublings of at least 20 (from P0 to P2) following the instructions and conditions provided by AMSBIO.
Applications
• perfect source for single-cell analysis from individual donors. • investigating the function and pathology of the respiratory system. • drug discovery cell screening for in vitro assay of compounds • 3D tissue model • gene expression • cell Based Assays among many others.
Advantages
- Convenience: P0 cells can be grown with any method amenable to expansion of primary airway epithelia.
- High purity and low passage
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells UMIX | 500k | View |
Proliferating Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells- P1 (NhBE-P1) are isolated, initially as NhBE-P0, from the bronchus at the bifurcation point to the fourth generation of bronchi. The original cell composition consisted of a mix of differentiated ciliated, non-ciliated, goblet, and basal cells. After culturing the mixed NhBE-P0 in BEGM, CRC or Dual Smad culture conditions, the result is a homogenous population of basal cells, or NhBE-P1.
Proliferating NhBE-P1 cells have been characterized by morphological assessment by light microscopy. These differentiated cells were characterized and Air/Liquid Interface culture (ALI) validated by immunofluorescence using protein markers for Cilia (acetylated tubulin), mucin (MUC5AC), tight junctions (Zonula Occludens-1), and basal cells (cytokeratin-5).
The NhBE-P1 cells are guaranteed to have minimum population doublings of at least 20 (from P1 to P3) following the instructions and conditions provided by AMSBIO.
Applications
• cell signaling • cell permeability • epithelial function • tissue repair • cytokine and growth factor production • apoptosis • pro-inflammatory signaling • mucin secretion • gene expression • Cell Based Assays among many others.
Advantages
- Convenience: P1 cells can be grown with any method amenable to expansion of primary airway epithelia including BEGM, CRC or Dual Smad conditions
- High purity and low passage
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells homogenous basal cell population at passage 1 | 500k | View |
Proliferating Normal Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells- P0 (NhSAE-P0) are isolated from the fifth generation of bronchi down to small airways near 1mm in diameter. The cell composition consists of undifferentiated ciliated, non-ciliated, goblet, and basal cells.
Proliferating NhSAE-P0 cells have been characterized and Air/Liquid Interface culture (ALI) validated by immunofluorescence using protein markers for Cilia (acetylated tubulin), mucin (MUC5AC), and tight junctions (Zonula Occludens-1).
The NhSAE-P0 cells are guaranteed to have minimum population doublings of at least 20 (from P0 to P2) following the instructions and conditions provided by AMSBIO.
Applications
• NhSAE-P0 cells can be used as a source for repeated differentiated cell stocks useful for any analysis procedure typically performed with freshly isolated cells derived from ex vivo tissue. • perfect source for single-cell analysis from individual donors. • investigating the function and pathology of the respiratory system. • 3D tissue model • gene expression • cell Based Assays • allow a researcher to perform FACS analysis of the diverse population of epithelial cells found within the tracheal cell composition among many others.
Advantages
- Convenience: P0 cells can be grown with any method amenable to expansion of primary airway epithelia.
- High purity and low passage
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells UMIX | 500k | View |
Proliferating Normal Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells- P1 (NhSAE-P1) are initially isolated as NhSAE-P0 cells from the fifth generation of bronchi down to small airways near 1mm in diameter. The NhSAE-P0 cells are then expanded on plastic using BEGM, CRC or Dual Smad expansion media to isolate out an homogenous basal cell population known as NhSAE-P1.
Proliferating NhSAE-P1 cells have been characterized by morphological assessment by light microscopy. These differentiated cells were characterized and Air/Liquid Interface culture (ALI) validated by immunofluorescence using protein markers for Cilia (acetylated tubulin), mucin (MUC5AC), tight junctions (Zonula Occludens-1), and basal cells (cytokeratin-5).
The NhSAE-P1 cells are guaranteed to have minimum population doublings of at least 20 (from P1 to P3) following the instructions and conditions provided by AMSBIO.
Applications
• cell signaling -cell permeability • epithelial function • tissue repair • cytokine and growth factor production • apoptosis • pro-inflammatory signaling • mucin secretion • gene expression • cell Based Assays among many others.
Advantages
- Convenience: P1 cells can be grown with any method amenable to expansion of primary airway epithelia including BEGM, CRC or Dual Smad conditions.
- High purity and low passage
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells homogenous basal cell population at passage 1 | 500k | View |
Proliferating Normal Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells- P0 (NhTE-P0) are isolated from the trachea of healthy human donors but do not contain epithelial cells from the primary bronchus. Each vial of the Proliferating NhTE-P0 cells contains the complete tracheal cell composition consisting of differentiated cells like ciliated and mucin producing cells as well as basal progenitor cells.
Proliferating NhTE-P0 cells have been characterized and Air/Liquid Interface culture (ALI) validated by immunofluorescence using protein markers for Cilia (acetylated tubulin), mucin (MUC5AC), tight junctions (Zonula Occludens-1), and basal cells (cytokeratin-5).
The NhTE-P0 cells are guaranteed to have minimum of at least 30 population doublings from passage number zero (P0) following the instructions and conditions provided by AMSBIO.
Applications
• NhTE-P0 cells can be used as a source for repeated differentiated cell stocks useful for any analysis procedure typically performed with freshly isolated cells derived from ex vivo tissue. • • perfect source for single-cell analysis from individual donors. • investigating the function and pathology of the respiratory system. • 3D tissue model • gene expression • cell Based Assays • allow a researcher to perform FACS analysis of the diverse population of epithelial cells found within the tracheal cell composition among many others.
Advantages
- Convenience: P0 cells can be grown with any method amenable to expansion of primary airway epithelia.
- High purity and low passage
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells UMIX | 500k | View |
Proliferating Normal Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells- P0 (NhTE-P1) are isolated as NhTE-P0 cells from the trachea of healthy human donors but do not contain epithelial cells from the primary bronchus. Each vial of the Proliferating NhTE-P1 cells were expanded on plastic using BEGM, CRC or Dual Smad expansion media to isolate out an homogenous basal cell population.
Proliferating NhTE-P1 cells have been characterized by morphological assessment by light microscopy. These differentiated cells were characterized and Air/Liquid Interface culture (ALI) validated by immunofluorescence using protein markers for Cilia (acetylated tubulin), mucin (MUC5AC), tight junctions (Zonula Occludens-1), and basal cells (cytokeratin-5).
The NhTE-P1 cells are guaranteed to have a minimum of at least 20 population doublings from P1 to P3 following the instructions and conditions provided by AMSBIO.
Applications
• cell signaling • cell permeability • epithelial function • tissue repair • cytokine and growth factor production • apoptosis • pro-inflammatory signaling • mucin secretion • gene expression • cell Based Assays among many others.
Advantages
- Convenience: P1 cells can be grown with any method amenable to expansion of primary airway epithelia including BEGM, CRC or Dual Smad conditions.
- High purity and low passage
- Access to high quality non-transplantable organs
- More extensive donor information
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells homogenous basal cell population at passage 1 | 500k | View |
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Human Lung Fibroblast; passage 2 | 500k | View |
Accessories
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| NB Hepatocyte Maintenance Medium; 250mL | 250 ml | View |
| NB Hepatocyte Plating Medium; 1000mL | 1000 ml | View |
| NB Hepatocyte Plating Medium; 250mL | 250 ml | View |
| NB Hepatocyte Thaw Medium (percol); 100mL | 100 ml | View |
| NB Hepatocyte Thaw Medium; 100mL | 100 ml | View |
| NB Kupffer Cell Maintenance Medium; 250mL | 250 ml | View |
| NB Kupffer Cell Plating Medium; 250mL | 250 ml | View |
| NB Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Growth Medium; 500mL | 500 ml | View |
| NB Stellate Growth Medium; 500mL | 500 ml | View |