Histones and Nucleosomes
AMSBIO offers both recombinant and purified nucleosomes, as well as full length versions of all the histone proteins. Some biotinylated histones and nucleosomes have been added to our continuously expanding product range.
The major difference between the recombinant proteins made in E.coli and those purified from whole cells is that the recombinant proteins are unmodified. E. coli and other bacteria do not have the enzymes to methylate or acetylate the histone proteins. Nucleosomes purified from mammalian cells will be methylated or acetylated on most histone sites. Our peptides are synthetic, they are methylated on specific sites, making them suitable substrates for our demethylases.
What are histones?
Histones are a family of basic proteins which closely associate with DNA in the nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Working to package and order the DNA, histones are the main protein components of chromatin, and also play a key role in gene regulation. There are 5 major families of histone proteins (H1 through H5). H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are known as the core histones while histones H1/H5 are called linker histones.
What are nucleosomes?
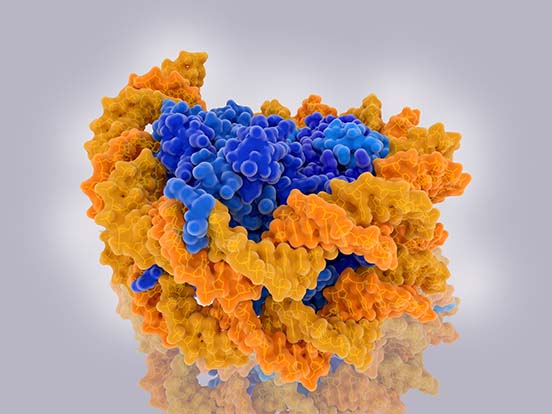
A nucleosome is the basic unit of DNA packaging. It consists of a segment of DNA wound around a core “octamer” of 8 histone proteins (two each of the core histones).
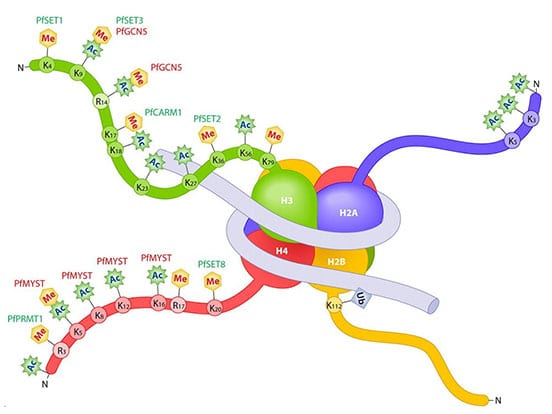
The “tails” of these histone proteins stick out, where they can be modified by a number of different histone acetyltransferases, methyltransferases, PARPs, and other epigenetic enzymes. Many of these enzymes modify very specific sites; for example, EZH2, specifically tri-methylates the lysine at position 27 in the H3 histone.
Nucleosomes are linked together by the H1/H5 linker histones to form a bead-like string of nucleosomes, which make up chromosomes.
| Name | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|
| Histone H2a|Full Length|Biotin-labeled|His-tag Recombinant | 0.5 mg | View |
| Histone H2a|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 1 mg | View |
| Histone H2a|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 100 ug | View |
| Histone H2b|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 1 mg | View |
| Histone H2b|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 100 ug | View |
| Histone H3 (2-58)|GST-tag Recombinant | 500 ug | View |
| Histone H3 peptide (1-21) | 160 nmol | View |
| Histone H3 peptide (21-44) | 160 nmol | View |
| Histone H3|Full Length|Biotin-labeled|His-tag | 0.5 mg | View |
| Histone H3|Full Length|Biotin-labeled|His-tag | 50 ug | View |
| Histone H3|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 1 mg | View |
| Histone H3|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 100 ug | View |
| Histone H4 (2-58)|GST-tag Recombinant | 500 ug | View |
| Histone H4 peptide (1-21) | 160 nmol | View |
| Histone H4|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 1 mg | View |
| Histone H4|Full Length|His-tag Recombinant | 100 ug | View |
| Histone Octamer (Full length) Recombinant | 100 ug | View |
| Histone Octamer (full length)|His-tag Recombinant | 100 ug | View |
| PRMT4 peptide substrate|Biotin-labeled | 80 nmol | View |