Heparinase
Enzymatic degradation for heparin and/or heparan sulfate
We provide heparinase enzymes (heparin lyase enzymes) isolated from natural strains of Flavobacterium heparinum. The specialised method of preparation produces exceptionally pure individual enzyme species by providing baseline separation between the three heparinases.
What We Offer
Heparinase I
- EC 4.2.2.7
- Degrades heparin and the S-domains of heparan sulfate.
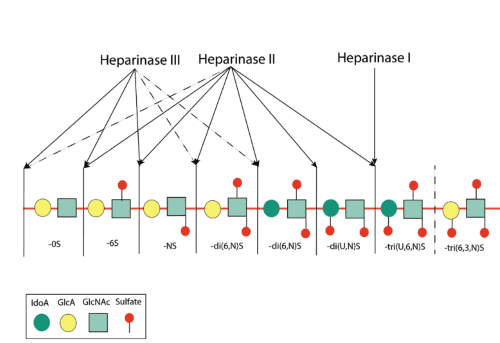
- Catalyses the eliminative scission of the glycosidic linkage between N-sulfated glucosamine (GlcNSO3) and 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid (IdoA,2SO3). The IdoA,2SO3residue is essential for the activity of Heparinase I while 6-O-sulfation of GlcNSO3 enhances enzyme activity.
Product Information Table
| Name | Datasheet | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heparinase I (EC 4.2.2.7) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 2 IU | 2 IU | View | |
| Heparinase I (EC 4.2.2.7) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 20 IU | - | 20 IU | View |
| Heparinase I (EC 4.2.2.7) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 200 IU | - | 200 IU | View |
| Heparinase I (EC 4.2.2.7) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 5 IU | 5 IU | View | |
| Heparinase I (EC 4.2.2.7) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 50 IU | - | 50 IU | View |
Heparinase II
- EC number not assigned
- Degrades heparin and heparan sulfate
- Catalyses the eliminative scission of the glycosidic linkages between N-sulfated or N-acetylated glucosamine and glucuronic or iduronic acid. This is a broad activity enzyme that tolerates O-sulfation of the uronic acid and glucosamine residues.
Heparinase III
- EC 4.2.2.8
- Degrades heparan sulfate (HS)
- Catalyses the eliminative scission of glycosidic linkages between N-sulfated or N-acetylated glucosamine (GlcNSO3or GlcNAc) and glucuronic acid (GlcA)

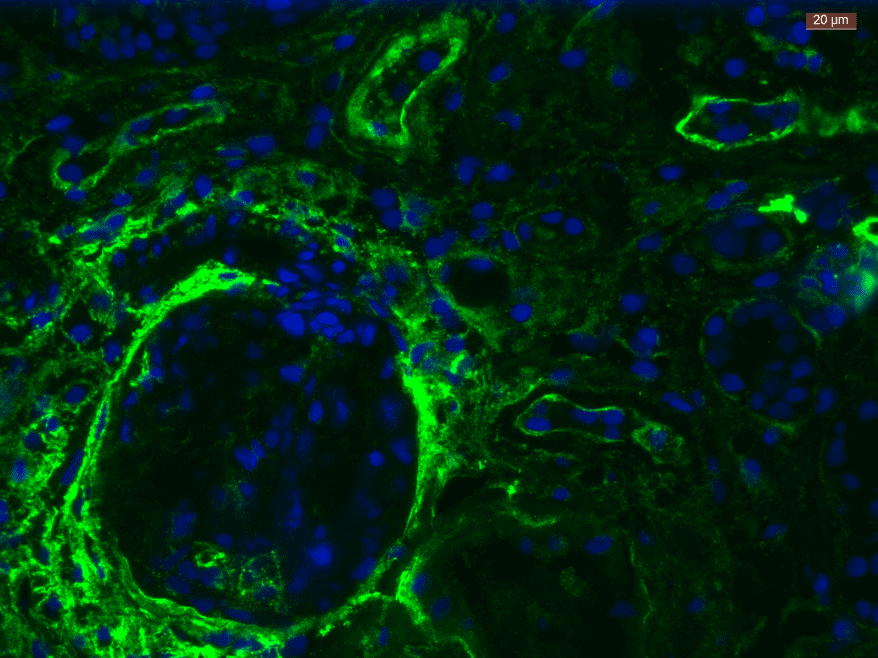
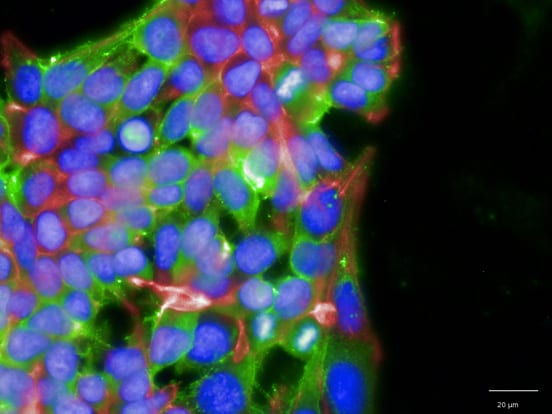
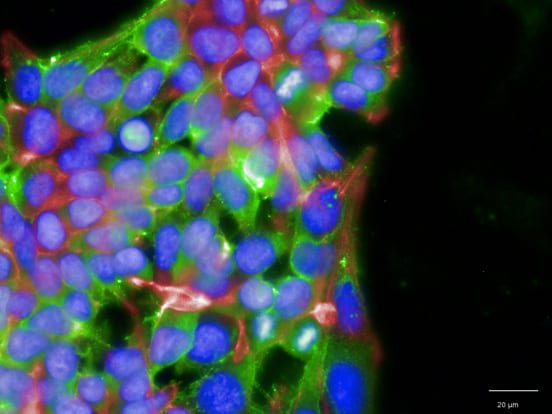
The investigation of viral entry receptors in lung organoids, such as heparan sulfate stained with AMSBIO α-heparan sulfate antibody (clone F58-10E4), allowed us to compare our model to adult human lung and discuss viral entry mechanisms. Importantly, AMSBIO also provides Heparinase III for enzymatic digest of the glycan receptor as negative staining control, which allows for an adequate staining control of improved quality compared to ‘primary ab only’ controls in challenging glycan receptor stains.
Helena Meyer-Berg (University of Oxford, UK)
Product Information Table
| Name | Datasheet | Packsize | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heparinase III (EC 4.2.2.8) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 0.5 IU | 0.5 IU | View | |
| Heparinase III (EC 4.2.2.8) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 1 IU | 1 IU | View | |
| Heparinase III (EC 4.2.2.8) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 2 IU | 2 IU | View | |
| Heparinase III (EC 4.2.2.8) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 20 IU | - | 20 IU | View |
| Heparinase III (EC 4.2.2.8) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 5 IU | 5 IU | View | |
| Heparinase III (EC 4.2.2.8) from Flavobacterium heparinum, 50 IU | - | 50 IU | View |
| Heparinase III (Heparitinase I) Flavobacterium heparinum (EC 4.2.2.8), 0.1 IU | - | 0.1 IU | View |
Can't find what you need?
Please contact us with any inquiries regarding our carbohydrate-related products